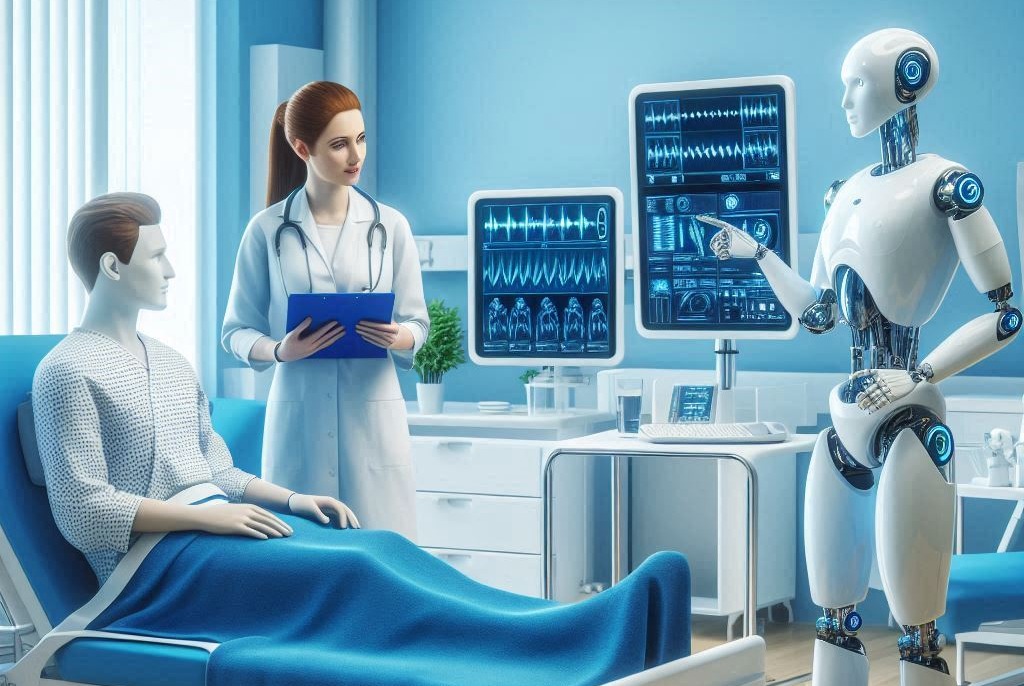
In a groundbreaking scientific development that could reshape the global healthcare landscape, China’s Tsinghua University has announced the creation of the world’s first fully virtual hospital managed entirely by advanced artificial intelligence systems, named “Agent Hospital.”
This project represents a major leap in the use of large language models, featuring 14 medical agents and 4 nursing agents working seamlessly to simulate a fully integrated healthcare environment.
These AI agents achieved a diagnostic accuracy rate of 93.06% in standardized tests—surpassing average human performance—and are capable of treating up to 10,000 patients in just a few days, an accomplishment that would take years using conventional healthcare systems.
Beyond improving clinical efficiency, this innovative initiative also serves as an advanced training platform for medical students, and as a simulation tool for epidemic scenarios and predictive outbreak modeling.
Designed as a digital medical city, the virtual hospital enables smooth interaction between virtual patients and intelligent agents, following a complete care cycle from registration to detailed follow-up.
Though still experimental, researchers see this as a radical transformation in medical practice, especially as these models continue to improve their ability to perform complex tasks in general medicine. However, specialties like psychiatry, neurology, and palliative care still require a human presence due to the emotional and empathetic dimensions that machines cannot yet replicate.
The team behind the project aims to eventually integrate the system as a virtual assistant within real hospitals, supporting doctors in diagnostic and treatment decisions while maintaining a delicate balance between human and machine roles.
The model also offers promising solutions for improving healthcare access in remote regions, where specialized medical professionals are often scarce.
Nonetheless, the path to widespread adoption raises serious ethical and legal questions, and will require strong digital infrastructure and user-friendly interfaces that build patient trust and ensure transparency.
Ultimately, the success of this model will depend on its ability to seamlessly integrate with existing healthcare systems, enabling safe and equitable use of its unprecedented capabilities.