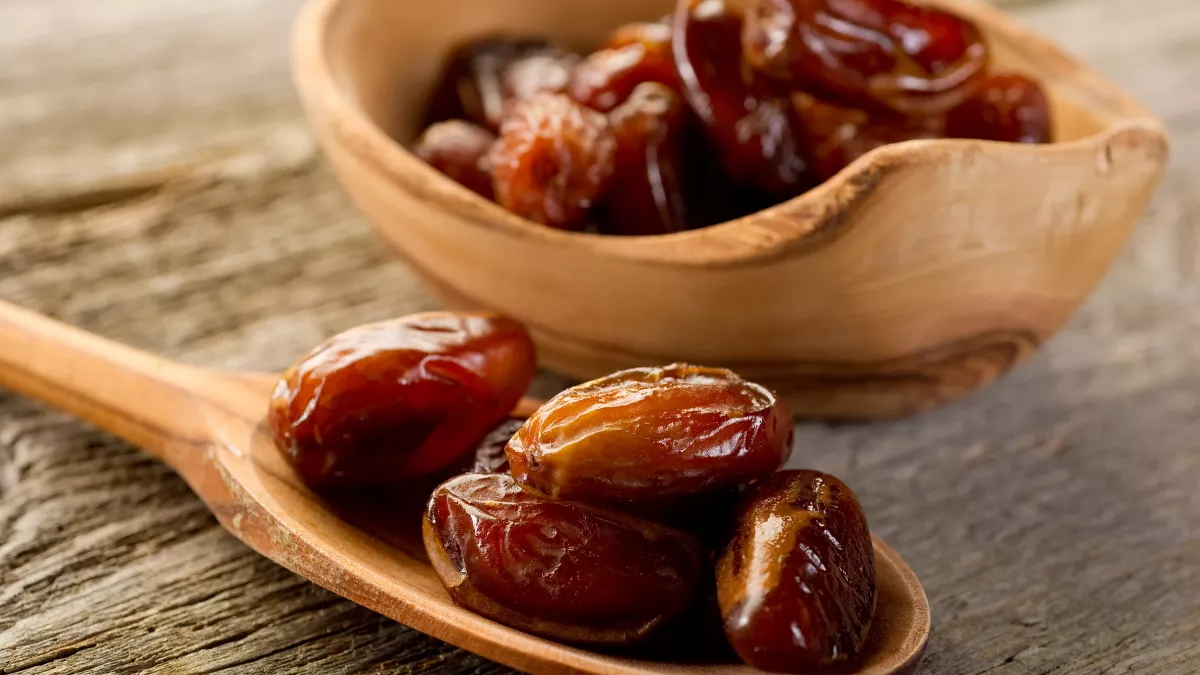
Dates are among the most popular fruits in the Arab world, and people often recommend eating them on an empty stomach for their supposed health benefits. But is this claim scientifically supported?
According to nutrition experts, there’s no scientific evidence proving that eating dates in the morning on an empty stomach provides any special benefits. However, dates remain a nutrient-rich fruit and a great addition to a healthy diet at any time of the day.
Dates are an excellent source of dietary fiber, which promotes healthy digestion and helps prevent constipation. They’re also packed with powerful antioxidants that fight free radicals and strengthen the immune system. In addition, dates are rich in potassium, which plays a key role in regulating blood pressure and supporting heart and muscle health.
They contain a variety of minerals such as iron, zinc, magnesium, and copper, though they’re relatively low in vitamins, offering only moderate amounts of B vitamins as well as vitamins A and C.
Because of their high natural sugar content, experts recommend eating dates in moderation, especially for people with diabetes or those following weight-management diets. Still, some research suggests that dates have a low glycemic index, meaning they don’t cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels.
Limited studies also indicate that dates may help relieve constipation and improve iron and hemoglobin levels in children and women, making them a good food for combating anemia.
During Ramadan, dates are the ideal choice for breaking the fast, as they quickly provide energy and minerals after long hours without food. Doctors also recommend moderate consumption for pregnant women, as dates may help ease labor and reduce constipation.
In conclusion, dates are a nutritious, well-balanced food, but eating them on an empty stomach doesn’t give them any “magical” effect. Their health benefits can be enjoyed whenever they’re consumed as part of a balanced diet.